Webpack-Flow
一 编译流程
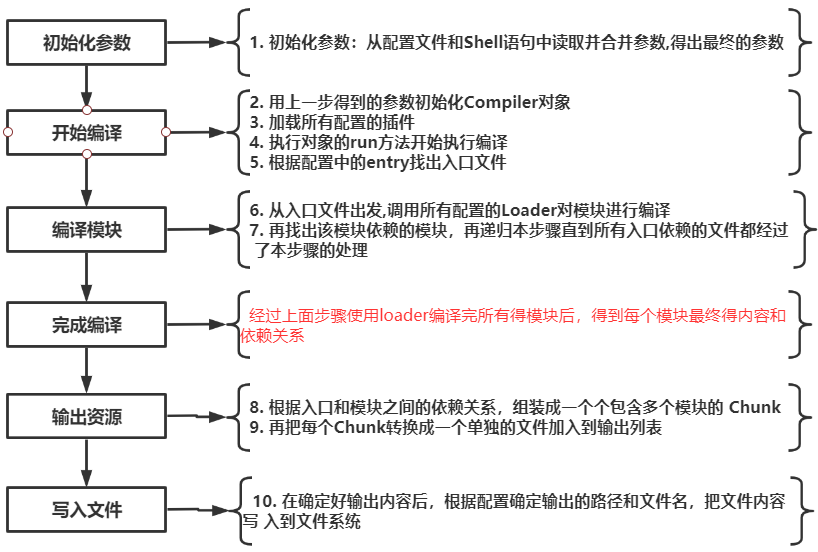
- 初始化参数:从配置文件和Shell语句中读取并合并参数,得出最终的配置对象
- 用上一步得到的参数初始化Compiler对象
- 加载所有配置的插件
- 执行对象的run方法开始执行编译
- 根据配置中的entry找出入口文件
- 从入口文件出发,调用所有配置的Loader对模块进行编译
- 再找出该模块依赖的模块,再递归本步骤直到所有入口依赖的文件都经过了本步骤的处理
- 根据入口和模块之间的依赖关系,组装成一个个包含多个模块的 Chunk
- 再把每个Chunk转换成一个单独的文件加入到输出列表
- 在确定好输出内容后,根据配置确定输出的路径和文件名,把文件内容写入到文件系统
TIP
在以上过程中,Webpack 会在特定的时间点广播出特定的事件,插件在监听到感兴趣的事件后会执行特定的逻辑,并且插件可以调用 Webpack 提供的 API 改变 Webpack 的运行结果
二 加载插件

1 运行入口
// debug.js
//1.引入核心模块
const webpack = require('./webpack');
//2.加载配置文件
const options = require('./webpack.config');
// 3. 执行webpack得到编译对象Compiler,就是一个大管理,是核心编译对象
const compiler = webpack(options);
// 4. 调用它的run方法开始启动编译
compiler.run();
2 配置文件
// webpack.config.js
const path = require('path');
const Run1Plugin = require('./plugins/run1-plugin')
const DonePlugin = require('./plugins/done-plugin')
module.exports = {
mode:'development',
entry: './src/index.js',
output:{
path:path.resolve(__dirname,'dist'),
filename: 'main.js' //'[name].js'
},
resolve:{
extensions:['.js','.jsx','.json']
},
module:{
rules:[
]
},
plugins:[
new Run1Plugin(),
new DonePlugin(),
]
}
3 webpack函数
// webpack/index.js
let Compiler = require('./Compiler');
function webpack(options) {
// 1. 初始化参数:从配置文件和Shell语句中读取并合并参数,得出最终的配置对象
// 1.1 获取shell命令中的参数
let shellConfig = process.argv.slice(2).reduce((shellConfig, item) => {
let [key, value] = item.split('=');
shellConfig[key.slice(2)] = value;
return shellConfig
}, {});
// 1.2 合并参数,得到最终配置对象
let finalOptions = {...options, ...shellConfig};
// 2. 用上一步得到的参数初始化Compiler对象
let compiler = new Compiler(finalOptions);
// 3. 加载所有配置的插件
if (finalOptions.plugins && Array.isArray(finalOptions.plugins)) {
// 有插件,就依次挂载所有的插件
for (const plugin of finalOptions.plugins) {
// 插件在webpack开始编译之前就全部挂载,也就是调用钩子的tap方法全部进行注册
// 但是插件需要等到插件关注的钩子触发的时候才会执行
plugin.apply(compiler);
}
}
return compiler;
}
module.exports = webpack;
4 compiler类
// webpack/Compiler.js
let {SyncHook} = require('tapable');
// 编译类
class Compiler {
constructor(options) {
this.options = options;
// 预设钩子集合
this.hooks = {
run: new SyncHook(), // 会在开始编译的时候触发
done: new SyncHook() // 会在完成编译的时候触发
}
}
// 4.执行对象的run方法开始执行编译
run() {
// 当调用run方法的时候会触发run这个钩子, 进而执行它的回调函调
this.hooks.run.call();
// 编译逻辑。。。
this.hooks.done.call();
}
}
module.exports = Compiler;
5 两个插件编写
// 1. plugins/run1-plugin.js
class RunPlugin {
constructor(options) {
this.options = options;
}
// 每个插件定死了有一个apply方法
// 每个插件的核心方法,用于webpack函数初始化挂载插件钩子
apply(compiler) {
// 监听感兴趣的钩子
compiler.hooks.run.tap('RunPlugin', () => {
console.log('RUN~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~');
})
}
}
module.exports = RunPlugin;
// 2. plugins/done-plugin.js
class DonePlugin {
constructor(options) {
this.options = options;
}
// 每个插件定死了有一个apply方法
apply(compiler) {
// 监听感兴趣的钩子
compiler.hooks.done.tap('DonePlugin', () => {
console.log('DONE~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~');
})
}
}
module.exports = DonePlugin;
6 执行命令输出结果
node debug.js
RUN~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
DONE~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
三 加载loader
1 编写四个loader
- loaders\logger1-loader.js
function loader(source){
console.log('logger1-loader');
return source+'//1';
}
module.exports = loader;
- loaders\logger2-loader.js
function loader(source){
console.log('logger2-loader');
return source+'//2';
}
module.exports = loader;
- loaders\logger3-loader.js
function loader(source){
console.log('logger3-loader');
return source+'//3';
}
module.exports = loader;
- loaders\logger4-loader.js
function loader(source){
console.log('logger4-loader');
return source+'//4';
}
module.exports = loader;
2 编译loader
- 核心思想:遍历入口文件,然后读取文件内容,根据后缀匹配文件名称,最后循环执行loader对源代码进行编译
// webpack\Compiler.js
let {SyncHook} = require('tapable');
const path = require('path');
const fs = require('fs');
// 编译类
class Compiler {
constructor(options) {
this.options = options;
// 预设钩子集合
this.hooks = {
run: new SyncHook(), // 会在开始编译的时候触发
done: new SyncHook() // 会在完成编译的时候触发
}
}
// 4.执行对象的run方法开始执行编译
run() {
// 当调用run方法的时候会触发run这个钩子, 进而执行它的回调函调
this.hooks.run.call();
// 5.根据配置中的entry找出入口文件,得到entry的绝对路径
// let entry = path.join(this.options.context, this.options.entry);
// console.log(entry);
// D:\web_project\webpack_demo\learnwebpackdemo\5.flow\src\index.js
// 找到入口文件,可能是字符,可能是对象》统一转化为对象
let entry = {};
if (typeof this.options.entry === 'string') {
entry.main = this.options.entry;
} else {
entry = this.options.entry;
}
for (const entryName in entry) {
// 统一不同操作系统的斜巷为 /
let entryFilePath = toUnixPath(path.join(this.options.context, entry[entryName]));
// 6.从入口文件出发,调用所有配置的Loader对模块进行编译
let entryModule = this.buildModule(entryFilePath);
}
this.hooks.done.call();
}
/**
* 编译模块
* 1. 读取模块内容
* @param {} modulePath
*/
buildModule(modulePath) {
// 读取原始源代码
let originalSourceCode = fs.readFileSync(modulePath, 'utf-8');
let targetSourceCode = originalSourceCode;
// 查找此模块对应的loader对代码进行转换
let loaders = [];
let rules = this.options.module.rules;
for (let i = 0; i < rules.length; i++) {
// 正则匹配上了模块的路径
if (rules[i].test.test(modulePath)) {
loaders = [...loaders, ...rules[i].use];
}
}
// loader需要倒着执行
// loaders=['logger1-loader.js','logger2-loader.js','logger3-loader.js','logger4-loader.js']
for (let i = loaders.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
let loader = loaders[i];
// 利用require加载loader方法,然后执行loader
targetSourceCode = require(loader)(targetSourceCode);
}
console.log('originalSourceCode:', originalSourceCode);
console.log('targetSourceCode:', targetSourceCode);
}
}
// path.posix.sep => /
// path.sep不同操作系统的路径分隔符 windows: \ mac和unix: /
function toUnixPath(filePath){
return filePath.replace(/\\/g, '/');
}
module.exports = Compiler;
- 打印结果
// node debug.js
RUN~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
logger4-loader
logger3-loader
logger2-loader
logger1-loader
originalSourceCode:
let title = require('./title');
console.log(title);
targetSourceCode:
let title = require('./title');
console.log(title);//4//3//2//1
DONE~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
四 依赖分析
- 利用@babel/parser把源代码转化为AST
- 利用@babel/traverse遍历AST,找到依赖模块节点进行替换
- 利用@babel/generator把AST重新转化为源代码
- 在线转AST-astexplorer
npm i babel-types @babel/generator @babel/parser @babel/traverse -D
const types = require('babel-types'); // 创建节点的库
const parser = require('@babel/parser'); // 源代码转成AST抽象语法树
const traverse = require('@babel/traverse').default; // 遍历语法树
const generator = require('@babel/generator').default; // 把语法树重新生成代码
/**
* 编译模块
* 1. 读取模块内容
* @param {} modulePath
*/
buildModule = (name, modulePath) => {
// 读取原始源代码
let originalSourceCode = fs.readFileSync(modulePath, 'utf-8');
let targetSourceCode = originalSourceCode;
// 查找此模块对应的loader对代码进行转换
let loaders = [];
let rules = this.options.module.rules;
for (let i = 0; i < rules.length; i++) {
// 正则匹配上了模块的路径
if (rules[i].test.test(modulePath)) {
loaders = [...loaders, ...rules[i].use];
}
}
// loader需要倒着执行
// loaders=['logger1-loader.js','logger2-loader.js','logger3-loader.js','logger4-loader.js']
for (let i = loaders.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
let loader = loaders[i];
// 利用require加载loader方法,然后执行loader
targetSourceCode = require(loader)(targetSourceCode);
}
// console.log('originalSourceCode:', originalSourceCode);
// console.log('targetSourceCode:', targetSourceCode);
// 7. 再找出该模块依赖的模块,再递归本步骤直到所有入口依赖的文件都经过了本步骤的处理
// 当前目录
let baseDir = toUnixPath(this.options.context);
let module = {
id: './' + path.posix.relative(baseDir, modulePath), // 模块ID
dependencies: [], // 依赖数组
name // 模块名称,为了方便chunk代码块做区分
};
// 原代码转化为ast,第一个参数源代码 第二个参数是表示一个模块
let astTree = parser.parse(targetSourceCode, {sourceType: 'module'});
// 遍历语法树,并找出require节点
traverse(astTree, {
CallExpression: ({node}) => {
if (node.callee.name === 'require') {
// 获取节点名称
let moduleName = node.arguments[0].value;
// 获取相对路径
// D:\web_project\webpack_demo\learnwebpackdemo\5.flow\src
let dirname = path.posix.dirname(modulePath);
// 要判断一个moduleName绝对路径还是相对路径,相对路径才需要下面的处理
let depModulePath;
if (path.isAbsolute(moduleName)) {
// 如果是绝对路径直接使用
depModulePath = moduleName;
}else{
// 如果是相对路径需要转化为绝对路径
// D:\web_project\webpack_demo\learnwebpackdemo\5.flow\src\title.js
depModulePath = path.posix.join(dirname, moduleName);
}
// 获取扩展名,进行查找依赖模块文件
let extensions = this.options.resolve.extensions;
depModulePath = tryExtensions(depModulePath, extensions, moduleName, dirname);
// 模块ID的问题 每个打包后的模块都会有一个moduleId,例如:"./src/title.js"
let depModuleId = './' + path.posix.relative(baseDir, depModulePath);
// 修改抽象语法树
node.arguments = [types.stringLiteral(depModuleId)];
module.dependencies.push(depModulePath);
}
}
});
// 根据新的语法树生成新代码
let {code} = generator(astTree);
module._source = code;// 转换后的代码 module moduleId dependencies _source
//再递归本步骤直到所有入口依赖的文件都经过了本步骤的处理
module.dependencies.forEach(dependency => {
let dependencyModule = this.buildModule(name, dependency);
this.modules.add(dependencyModule);
});
return module;
}
五 多入口编译
- 配置多入口
// webpack.config.js
const path = require('path');
const Run1Plugin = require('./plugins/run1-plugin')
const DonePlugin = require('./plugins/done-plugin')
module.exports = {
mode:'development',
devtool:'inline-source-map',
context:process.cwd(),//根目录 current working directory
entry:{
page1:'./src/page1.js',
page2:'./src/page2.js'
},
output:{
path:path.resolve(__dirname,'dist'),
filename: '[name].js'
},
resolve:{
extensions:['.js','.jsx','.json']
},
module:{
rules:[
{
test:/\.js$/,
use:[
path.resolve(__dirname,'loaders','logger1-loader.js'),
path.resolve(__dirname,'loaders','logger2-loader.js'),
]
},
{
test:/\.js$/,
use:[
path.resolve(__dirname,'loaders','logger3-loader.js'),
path.resolve(__dirname,'loaders','logger4-loader.js'),
]
}
]
},
plugins:[
new Run1Plugin(),
new DonePlugin(),
]
}
- 新建入口文件
// src\page1.js
let title = require('./title');
console.log(title);
// src\page2.js
let title = require('./title');
console.log(title);
- 写入文件
// webpack\Compiler.js
let {SyncHook} = require('tapable');
const path = require('path');
const fs = require('fs');
const types = require('babel-types'); // 创建节点的库
const parser = require('@babel/parser'); // 源代码转成AST抽象语法树
const traverse = require('@babel/traverse').default; // 遍历语法树
const generator = require('@babel/generator').default; // 把语法树重新生成代码
// 编译类
class Compiler {
constructor(options) {
this.options = options;
// 预设钩子集合
this.hooks = {
run: new SyncHook(), // 会在开始编译的时候触发
done: new SyncHook() // 会在完成编译的时候触发
}
this.modules = new Set(); // 这里存放着所有的模块
this.chunks = new Set(); // 存放所有的代码块
this.assets = {}; // 输出列表 存放着将要产出的资源文件
this.files = new Set(); // 表示本次编译的所有产出的文件名
this.entries = new Set();// 这个数组存放着所有的入口
}
// 4.执行对象的run方法开始执行编译
run() {
// 当调用run方法的时候会触发run这个钩子, 进而执行它的回调函调
this.hooks.run.call();
// 5.根据配置中的entry找出入口文件,得到entry的绝对路径
// let entry = path.join(this.options.context, this.options.entry);
// console.log(entry);
// D:\web_project\webpack_demo\learnwebpackdemo\5.flow\src\index.js
// 找到入口文件,可能是字符,可能是对象》统一转化为对象
let entry = {};
if (typeof this.options.entry === 'string') {
// 如果字符串,默认为main
entry.main = this.options.entry;
} else {
entry = this.options.entry;
}
for (const entryName in entry) {
// 统一不同操作系统的斜巷为 /
let entryFilePath = toUnixPath(path.join(this.options.context, entry[entryName]));
// 6.从入口文件出发,调用所有配置的Loader对模块进行编译
let entryModule = this.buildModule(entryName, entryFilePath);
// 8.根据入口和模块之间的依赖关系,组装成一个个包含多个模块的 Chunk
let chunk = {
name: entryName,
entryModule,
modules: new Set([...this.modules].filter(module => module.name === entryName))
// 过滤入口名称相同的代码块切分到一起
};
this.chunks.add(chunk);
this.entries.add(chunk); // 也是入口代码块
}
// 9.再把每个Chunk转换成一个单独的文件加入到输出列表
//一个 chunk会成为this.assets对象的一个key value
//一个chunk对应this.assets的一个属性,而每个assets属性会对应一个文件file
/* this.chunks.forEach(chunk=>{
//key文件名 值是打包后的内容
let filename = this.options.output.filename.replace('[name]',chunk.name);
let targetPath = path.join(this.options.output.path,filename);//page1.js page2.js
fs.writeFileSync(targetPath,getSource(chunk));
}); */
// console.log(this.chunks);
this.chunks.forEach(chunk => {
let filename = this.options.output.filename.replace('[name]', chunk.name);
// key文件名 值是打包后的内容
this.assets[filename] = getSource(chunk);
});
// this.hooks.emit.call();
// 10.在确定好输出内容后,根据配置确定输出的路径和文件名,把文件内容写入到文件系统
this.files = Object.keys(this.assets);//['main.js']
// 存放本次编译输出的目标文件路径
for(let file in this.assets){
let targetPath = path.join(this.options.output.path, file);//page1.js page2.js
fs.writeFileSync(targetPath, this.assets[file]);
}
this.hooks.done.call();
}
/**
* 编译模块
* 1. 读取模块内容
* @param {} modulePath
*/
buildModule = (name, modulePath) => {
// 读取原始源代码
let originalSourceCode = fs.readFileSync(modulePath, 'utf-8');
let targetSourceCode = originalSourceCode;
// 查找此模块对应的loader对代码进行转换
let loaders = [];
let rules = this.options.module.rules;
for (let i = 0; i < rules.length; i++) {
// 正则匹配上了模块的路径
if (rules[i].test.test(modulePath)) {
loaders = [...loaders, ...rules[i].use];
}
}
// loader需要倒着执行
// loaders=['logger1-loader.js','logger2-loader.js','logger3-loader.js','logger4-loader.js']
for (let i = loaders.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
let loader = loaders[i];
// 利用require加载loader方法,然后执行loader
targetSourceCode = require(loader)(targetSourceCode);
}
// console.log('originalSourceCode:', originalSourceCode);
// console.log('targetSourceCode:', targetSourceCode);
// 7. 再找出该模块依赖的模块,再递归本步骤直到所有入口依赖的文件都经过了本步骤的处理
// 当前目录
let baseDir = toUnixPath(this.options.context);
let module = {
id: './' + path.posix.relative(baseDir, modulePath), // 模块ID
dependencies: [], // 依赖数组
name // 模块名称,为了方便chunk代码块做区分
};
// 原代码转化为ast,第一个参数源代码 第二个参数是表示一个模块
let astTree = parser.parse(targetSourceCode, {sourceType: 'module'});
// 遍历语法树,并找出require节点
traverse(astTree, {
CallExpression: ({node}) => {
if (node.callee.name === 'require') {
// 获取节点名称
let moduleName = node.arguments[0].value;
// 获取相对路径
// D:\web_project\webpack_demo\learnwebpackdemo\5.flow\src
let dirname = path.posix.dirname(modulePath);
// 要判断一个moduleName绝对路径还是相对路径,相对路径才需要下面的处理
let depModulePath;
if (path.isAbsolute(moduleName)) {
// 如果是绝对路径直接使用
depModulePath = moduleName;
}else{
// 如果是相对路径需要转化为绝对路径
// D:\web_project\webpack_demo\learnwebpackdemo\5.flow\src\title.js
depModulePath = path.posix.join(dirname, moduleName);
}
// 获取扩展名,进行查找依赖模块文件
let extensions = this.options.resolve.extensions;
depModulePath = tryExtensions(depModulePath, extensions, moduleName, dirname);
// 模块ID的问题 每个打包后的模块都会有一个moduleId,例如:"./src/title.js"
let depModuleId = './' + path.posix.relative(baseDir, depModulePath);
// 修改抽象语法树
node.arguments = [types.stringLiteral(depModuleId)];
module.dependencies.push(depModulePath);
}
}
});
// 根据新的语法树生成新代码
let {code} = generator(astTree);
module._source = code;// 转换后的代码 module moduleId dependencies _source
//再递归本步骤直到所有入口依赖的文件都经过了本步骤的处理
module.dependencies.forEach(dependency => {
let dependencyModule = this.buildModule(name, dependency);
this.modules.add(dependencyModule);
});
return module;
}
}
// path.posix.sep => /
// path.sep不同操作系统的路径分隔符 windows: \ mac和unix: /
function toUnixPath(filePath){
return filePath.replace(/\\/g, '/');
}
/**
* 匹配后缀查找文件
* @param {*} modulePath 依赖模块
* @param {*} extensions 后缀数组
* @param {*} originalModulePath 模块名称
* @param {*} moduleContext 相对路径
*/
function tryExtensions(modulePath, extensions, originalModulePath, moduleContext){
for (let i = 0; i < extensions.length; i++) {
if (fs.existsSync(modulePath + extensions[i])){
return modulePath+extensions[i];
}
}
throw new Error(`Module not found: Error: Can't resolve '${originalModulePath}' in '${moduleContext}'`);
}
//let chunk = {name:'main',entryModule,modules:this.modules};
function getSource(chunk){
return `
(() => {
var modules = {
${
[...chunk.modules].map(module=>`
"${module.id}": (module,exports,require) => {
${module._source}
}`).join(',')
}
};
var cache = {};
function require(moduleId) {
if (cache[moduleId]) {
return cache[moduleId].exports;
}
var module = (cache[moduleId] = {
exports: {},
});
modules[moduleId](module, module.exports, require);
return module.exports;
}
(() => {
${chunk.entryModule._source}
})();
})();
`;
}
module.exports = Compiler;